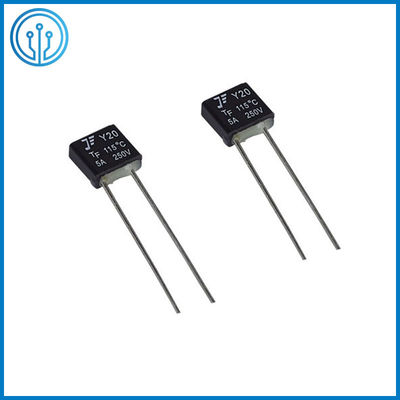
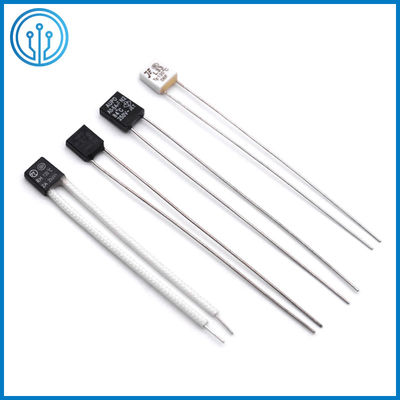
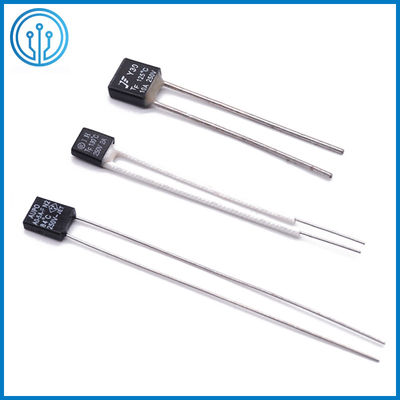
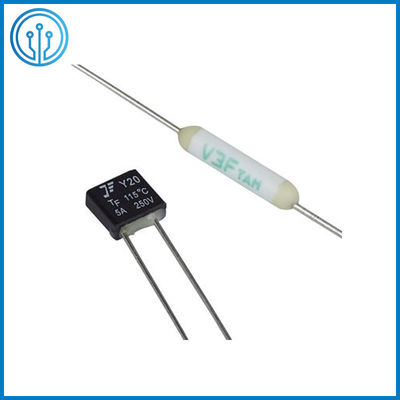
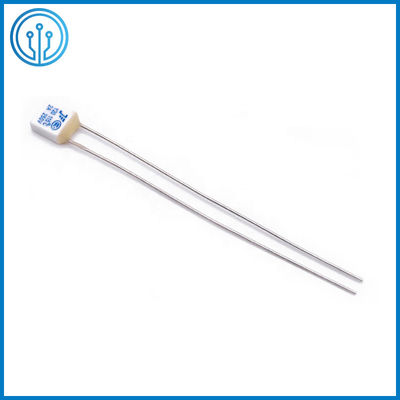
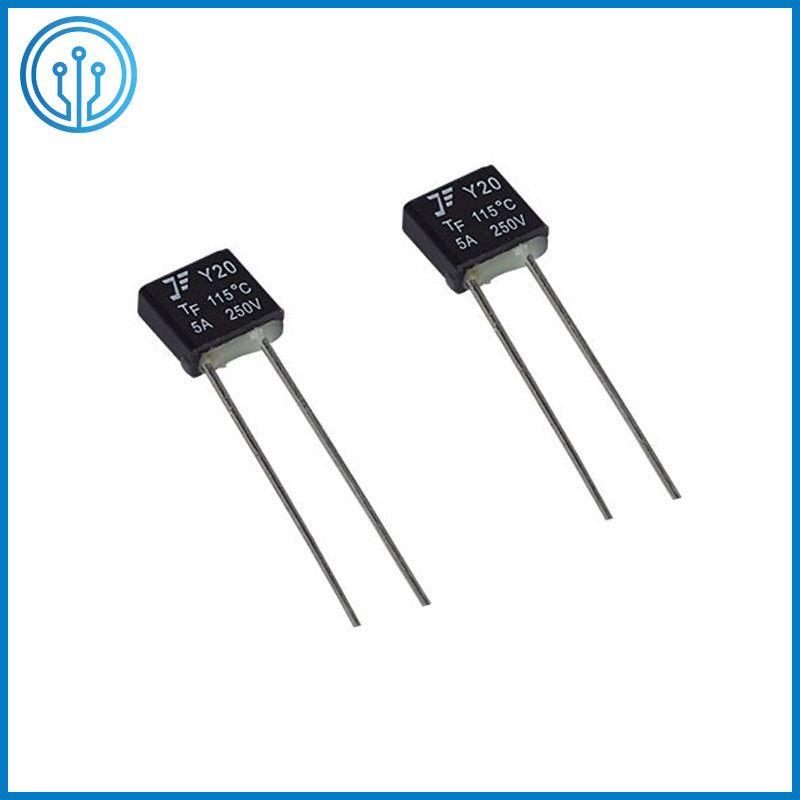
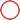
5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C Radial Lead Thermal Cutoff Fuse
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | DONGGUAN,GUANGDONG,CHINA |
| Brand Name: | FUSEI |
| Certification: | CQC/CCC/UL |
| Model Number: | Y 5A 250V |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1000PCS |
|---|---|
| Price: | Negotiable |
| Packaging Details: | Bulk,1000pcs per bag |
| Delivery Time: | 7-10 workdays |
| Payment Terms: | T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability: | 50000pcs per day |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Name: | Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V | Rated Current: | 5A |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rated Voltage: | 250V | Housing: | Insulated Plastic |
| Alloy: | Low Melting Point Alloy | Coating: | Special Resin |
| Lead: | Tinned Plated Copper | Certifications: | UL,CCC,CQC |
| Rated Operating Temperature Tf: | 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C | Limit Temperature: | 180 Deg |
| High Light: | 5A 250V Thermal Cutoff Fuse,125C Thermal Cutoff Fuse,130C Radial Lead Fuse |
||
Product Description
Coffee Maker Radial Leaded Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C For Fan Motor Overheating Protection
1 Product description Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
A thermal fuse or thermal cutoff is a safety device which open circuits against overheat. It detects the heat caused by the over-current due to short circuit or component breakdown. Thermal fuses do not reset themselves when the temperature drops like a circuit breaker would.
Y series thermal fuse introduction: thermal fuse is composed of fuse wire and insulated shell, mainly used in electrical and electronic product equipment and its parts. It is mostly used in indoor electrical equipment, mainly to protect electrical equipment from overheating under abnormal conditions. Once the fuse is to be reset, only the temperature fuse of the same type and specification can be used.
2 Working principle Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
When the temperature of the equipment rises abnormally, the thermal fuse is induced to heat, and when the temperature reaches the set temperature of the alloy, the low melting point is melted, and the surface tension of the molten alloy increases under the action of the special resin, causing the alloy to shrink in a spherical shape. On the lead wire, the circuit is completely cut off.
3 Anatomy Diagram Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
![]()
| a | b | c | d | e |
| Insulation Case | Low melting point alloy |
Special resin |
Seal resin |
Tinned plated copper |
4 Product installation guidelines Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
![]()
* Keep a distance of 3mm from the fuse body when bending the wire.
* When welding or soldering exceeds the rated temperature of the fuse, the longer the welding distance and the shorter the welding time, the less damage to the fuse.
* Be careful of the current flowing in the insurance body.
* Do not use liquids or toxic gases such as sulfuric acid and nitric oxide.
* Do not connect the heater and the fuse directly.
5 Dimension Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C (mm)
![]()
| A | B | C | D | E※ |
| 8.5±0.5 | 8.0±0.2 | 3.5±0.2 | 1.0±0.05 | 45±2 |
|
Length can be customized on request |
||||
6 Electrical Performances Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
| P/N |
Rated operating temperature Tf(℃) |
Actual operating temperature (℃) |
Hold temperature Tc(℃) |
Limit temperature Tm(℃) |
Rated Voltage (V) |
Rated Current (A) |
| Y10 | 102 | 98±1 | 72 | 150 | 250 | 10 |
| Y20 | 115 | 111±2 | 87 | 150 | 250 | 10 |
| Y30 | 125 | 121±2 | 95 | 150 | 250 | 10 |
| Y35 | 130 | 126±1 | 102 | 150 | 250 | 10 |
| Y50 | 150 | 146±2 | 120 | 180 | 250 | 10 |
7 Company Introduction Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
* Our company is located in Shilong Town, Dongguan City, Guangdong Province. It is a high-tech enterprise specializing in the production of thermal fuses.
* Since its establishment, the company has been committed to the development, production and application of thermal fuses. The products have passed CCC, VDE, TUV, UL, SGS certification, and the quality system has passed ISO9000 certification. The company has independent development capabilities and can develop various products required by customers in accordance with customer requirements. At present, the company's research and development capabilities, production control, product quality, and quality assurance capabilities have reached the advanced level in the same industry.
* The RH temperature fuse produced by our company is suitable for power transformers, power switches, sockets, rectifiers, fitness massagers, electric blankets, energy-saving lamps, communication tools and other household appliances. It is an indispensable safety for protecting electrical products and preventing electrical fires. Accessories. To
* The company adheres to the principle of "doing the job well the first time", with fast delivery as the main line, and reasonable price as the competitiveness, to provide manufacturers with satisfactory products and services.
8 Quality Assurance Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
![]()
9 More Products Of The Thermal Cutoff Fuse 5A 250V 102C 115C 125C 130C 150C
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
10 Some Frequently Asked Questions about Thermal Fuse
An electric fuse is a common name of a thermal fuse. The thermal fuse is of two types.
The one which melts at a certain high temperature
The one which disconnects due to sub-zero temperature as required.
Hypo thermal fuse is made of Biometal but a simple electric thermal fuse can be of any metal or alloy.
There is another fuse that does not blow but disconnects the electric circuit. This is called a magnetic fuse. This used in circuit breaker.
2. Are thermal fuses universal?
If by “universal” you mean “one size fits all”, then no. Thermal fuses come in a range of temperatures. The only ones I’ve bought are to replace failed ones in coffee makers, and I picked ones rated at around 110*C with an appropriate current capacity. Did not search for anything else, but higher current capacity units must exist.
For those who have not run into these devices, they operate like any other fuse in that they are installed in series with the power source, but are designed to be relatively insensitive to current and to open when their temperature exceeds the design point. A valuable safety device in heated appliances.
3. How do I test a dryer thermal fuse?
First of all, understand that once a certain amount of current goes through any kind of fuse, the fuse blows and can only be replaced, not repaired. So then, the only test you really want to do is to see if the fuse can still conduct electricity. Unplug the power cable and disconnect either end of the thermal fuse. Connect any cheap ohm meter to the loose end and the other end. If you get a reading, you may consider the fuse to be good. Don’t have a meter? In that case, you can use an old flashlight bulb (not LED), along with a battery and a piece of wire to test the fuse. Press the base of the bulb against one node of the battery while pressing the opposite end of the battery to one of the 2 fuse connections. At the same time, hold a test wire between the side of the bulb and the other fuse wire. If the fuse is good, the light will turn on.
4. How do I know if my thermal fuse is blown?
Using a digital or analog multimeter, or other resistance-measuring instruments, check the resistance across the thermal fuse (preferably when it’s out of the circuit, which can affect the reading), If you read continuity (in the range of several ohms or less, depending on its rating), the fuse is still functional. If you read an open circuit, the fuse is blown, and has to be replaced.
5. How do you test a fuse using a multimeter?
Testing connectivity is the best way of testing a fuse. A fuse works as long as its two terminals are connected by wire i.e. the two terminals of the fuse are shorted.
If the connectivity test fails then it is sure that the fuse isn’t working. However, there might arise a case if the fuse isn’t using proper material. There might not be any connectivity, however, testing the resistance between the two terminals would give a small non-zero value. Even in such cases, we say that the fuse is working. However, such cases rarely exist and if they do we don’t consider as a good fuse (at least for the small power applications like a household)
6. What is the function of the thermal fuse of an electric fan?
When the oil in the cheap sleeve bearings in the cheap shaded pole motor gets gummy, the motor will start drawing more current and run hotter. If the motor is not re-lubricated in a timely manner, eventually the sleeve bearings will get stuck and the rotor will fail to turn. This results in a locked-rotor condition and the windings draw more current and produce more heat than they can dissipate with no airflow over them to provide cooling. Eventually, the enamel insulation degrades and gets hot enough to smoke, possibly producing shorted turns that draw even more current.
The thermal fuse is a safety device to prevent the cheap motor from actually catching on fire. Sometimes the fuse can be replaced and the bearings can be relubricated to get another year or two of service if the windings haven’t discolored from overheating, but you can be sure that the end is near. You are better off getting a fan motor with sealed ball bearings. They cost more but last much longer, and usually give you a warning by making a rattling noise when the bearings start to wear out rather than seizing silently.
7. What material is used for making electrical fuses and why?
Electrical fuses are generally made from materials having low melting. It acts as a low resistance path when the current flowing through it exceeds its rating by even a small amount. This is done to protect an electrical device from getting damaged. Thus, it acts as an overcurrent protection device. During faults, especially short circuit faults, when heavy currents suddenly flow, the fuse wire gets heated up and melts down, thereby preventing damage and fires from occurring. The fuse wires in general are made of nichrome, etc.
8. What is a fuse?
It’s a safety device used to provide overcurrent protection of a circuit. Its main component is a metal wire
9. What is the difference between fuse and circuit breaker?
Fuse-it is such a type of device which breaks the circuit one time when overcurrent in the circuit. you cannot break the circuit or open-close according to your choice.
Breaker-it is such type of electrical equipment which breaks when overcurrent, other faulty conditions in the circuit. you can easily control the breaker for opening and closing the circuit ut is such a type of automatic switch. Mainly the big breakers are mainly run with the help of a relay.
10. What causes fuses to blow?
A fuse is a safety device that should protect the rest of the circuit from (more) damage when there is a FAULT in the circuit. This can be caused by:
component failure
placing a load in the circuit that exceeds the Circuits safe level.
Note that some circuits (example: motors) can have a very large starting current and special (slow blow) fuses are designed for this type of load.
wiring failure
placing a load in the circuit that exceeds the Circuits safe level.
Note that some circuits (example: motors) can have a very large starting current and special (slow blow) fuses are designed for this type of load.
is generally connected in series in the circuit when it is used. Therefore, when choosing a thermal fuse, its rated current must be greater than the current used in the circuit. Never allow the current through the thermal fuse to exceed the specified rated current. Before selecting the rated temperature of the thermal fuse, you must understand and measure the temperature difference between the temperature to be protected and the location where the planting fuse is installed.
In addition, the length of the fusing time and the availability of ventilation are also closely related to the selection of the rated temperature of the thermal fuse.