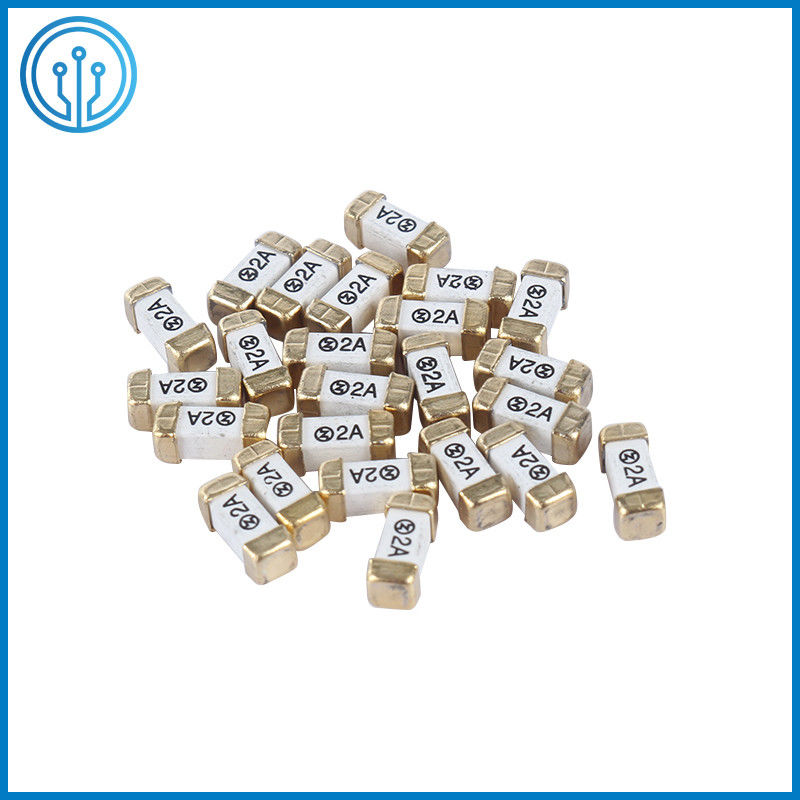
2-SMD Board Mount Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
Product Details:
| Place of Origin: | Dongguan,Guangdong,China |
| Brand Name: | AMPFORT |
| Certification: | UL,CUL,ROHS,REACH |
| Model Number: | SRT1630 |
Payment & Shipping Terms:
| Minimum Order Quantity: | 1000 Pcs |
|---|---|
| Price: | Contact Ampfort sales |
| Packaging Details: | Bulk, 1000 pieces per reel |
| Delivery Time: | 10 Workdays |
| Payment Terms: | Paypal, T/T, Western Union |
| Supply Ability: | 15,000,000 Pieces Per Month |
|
Detail Information |
|||
| Product Name: | Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V | Size: | 2410/1808/6125 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Current: | 6.3A | Voltage: | 350V |
| Response Time: | Slow Blow | Standard: | UL 248-14 |
| UL File Number: | E340427 | Mounting Type: | Surface Mount |
| Package: | 2-SMD, Square End Block | Breaking Capacity @ Rated Voltage: | 35A@350VAC |
Product Description
2-SMD Board Mount Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
Description Of The Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
Slow Blow Surface Mounted Fuse designed as UL248-14, is chosen as overcurrent protection in various electrical circuit especially power supply and LED driver since can withstand high inrush surge current .To ensure quality, gold plated cap can be choosed for soldering safety . If PCB is single plate, you can choose cheaper one - sliver plated cap.
Application Of The Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
♦ LED Driver
♦ Power Adapter
♦ Power Supply
♦ Telecom product
♦ Security system
♦ LED lighting
♦ Monitor LCD LED
Fusing Time Of The Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
![]()
| % of Ampere Rating(In) | Blowing Time |
| 100% * In | 4 hours Min |
| 200% * In | 120 sec Max |
| 1000% * In | 10ms Min |
Electrical Specifications Of The Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
Breaking Capacity: 35A@350Vac 50A@300Vac, 50A@250Vac,200A@125Vac.
|
Catalog No. |
Ampere Rating |
Voltage Rating |
Breaking Capacity |
Nominal Cold Resistance (Ohms) |
I2TMelting Integral(A2.S) |
| SRT0250 | 250mA | 350V |
35A@350VAC 50A@300VAC 50A@250VAC 200A@125VAC |
0.860 | 0.145 |
| SRT0300 | 300mA | 350V | 0.620 | 0.162 | |
| SRT0315 | 315mA | 350V | 0.550 | 0.189 | |
| SRT0375 | 375mA | 350V | 0.470 | 0.200 | |
| SRT0400 | 400mA | 350V | 0.380 | 0.238 | |
| SRT0500 | 500mA | 350V | 0.320 | 0.275 | |
| SRT0600 | 600mA | 350V | 0.285 | 0.470 | |
| SRT0630 | 630mA | 350V | 0.256 | 0.566 | |
| SRT0700 | 700mA | 350V | 0.208 | 0.805 | |
| SRT0750 | 750mA | 350V | 0.175 | 1.240 | |
| SRT0800 | 800mA | 350V | 0.155 | 1.880 | |
| SRT1100 | 1A | 350V | 0.148 | 3.500 | |
| SRT1125 | 1.25A | 350V | 0.102 | 4.760 | |
| SRT1150 | 1.5A | 350V | 0.085 | 6.305 | |
| SRT1160 | 1.6A | 350V | 0.075 | 6.505 | |
| SRT1200 | 2A | 350V | 0.044 | 8.950 | |
| SRT1250 | 2.5A | 350V | 0.043 | 16.025 | |
| SRT1300 | 3A | 350V | 0.033 | 21.560 | |
| SRT1315 | 3.15A | 350V | 0.029 | 22.750 | |
| SRT1350 | 3.5A | 350V | 0.027 | 27.050 | |
| SRT1400 | 4A | 350V | 0.025 | 31.808 | |
| SRT1500 | 5A | 350V | 0.019 | 40.250 | |
| SRT1600 | 6A | 350V | 0.018 | 67.245 | |
| SRT1630 | 6.3A | 350V | 0.017 | 73.550 | |
| SRT1700 | 7A | 350V | 0.015 | 76.280 |
Frequently Asked Questions about Fuse Resistors Tech Of The Square End Block Slow Blow Cartridge Surface Mount Fuse 6.3A 350V
1. Do fuses act as resistors?
A resistor limits current by its value of resistance measured in ohms. A fuse limits overcurrent damage by opening the circuit above a certain current value. ... A fuse can be used as a resistor. There are even fusible resistors, which act as a resistor with a definite value but they also act like a fuse on overcurrent.
2. What is a fusible resistor?
The fusible resistor is a special type of resistor made for the purpose of the protection of any circuit. ... A fusible resistor is useful for highly sensitive circuits of lower power requirements and applications where the overload and surge handling requirements are not too severe.
3. How do fusible resistors work?
A fusible resistor opens like a fuse when its current rating is exceeded. The component is generally a nichrome element with a melting temperature of around 1,400°C. Nichrome has a low thermal coefficient of resistance which allows the resistor to have a stable resistance over temperature.
4. What is the resistance of a fuse?
Next question: how much resistance has a fuse? Well, it depends on its type and on its voltage, current and I2t ratings. The nominal "cold" resistance (i.e., at < 10% rated current) can range from < 10 milliOhms up to several Ohms.
5. How do you calculate resistance of a fuse?
Rearranging the formula V=IR to I=V/R allows substituting V/R for I in P=IV yielding P=V^2/R and rearranging for R yields R=V^2/P. For the fuse: The fuse amperage is usually inscribed on the outside of the fuse; the element has very little resistance, but it's resistance could be measured with a multi-meter.
6. Why does fuse have high resistance?
A fuse wire should have high resistance, and a lot of heat is generated and it is easier for the fuse wire to reach its melting point. Also, a high resistance decreases the current flowing in the circuit than what would have been in the absence of it.
7. What is a fuse resistor?
A Fusible Resistor is a wire-wound resistor that is designed to burn open easily when the power rating of the resistor is exceeded.
8. What is the function of a fusible resistor?
A resistor designed to protect a circuit against overload; its resistance limits current flow and thereby protects against surges when power is first applied to a circuit; its fuse characteristic opens the circuit when the current drain exceeds design limits.
9. Can you use a fuse instead of a resistor?
A fuse can be used as a resistor. There are even fusible resistors, which act as a resistor with a definite value but they also act as a fuse on overcurrent. ... A resistor limits current by its value of resistance measured in ohms. A fuse limits overcurrent damage by opening the circuit above a certain current value.
10. Does a fuse add resistance?
Yes, it will, because any real-world fuse has resistance. And this resistance will also change with temperature.